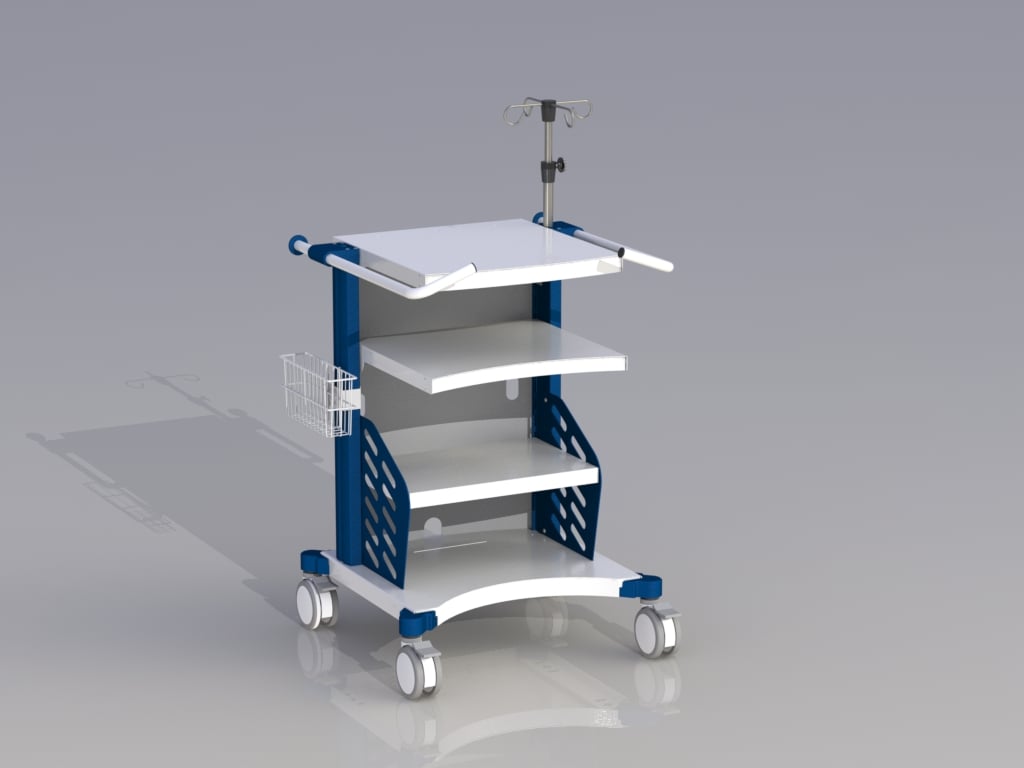
What features are ideal for housing arthroscopic surgery equipment on a medical cart?
Arthroscopic surgery is a blanket term that encompasses a variety of procedures on patients’ joints. Arthroscopic procedures may be diagnostic or may treat the patient through knee surgery, hip surgery, or procedures for the shoulder, elbow, or wrist. The arthroscopic surgeon may have to repair torn tissues, tendons, or ligaments, or remove bone fragments that are affecting the patient’s range of motion.
There are hundreds of thousands of arthroscopic surgeries performed every year in the United States and millions estimated worldwide. When it comes to the best cart to use to mount or store equipment for arthroscopic surgery, there are some important factors and functions to consider.
If you are designing a device or suite of devices for use in arthroscopic surgery, you will need a cart that can meet these unique needs. Read on for more information about each design factor and considerations for the cart itself.
Key Factor #1: Safely managing equipment weight
Based on our experience with previous medical cart projects for arthroscopic applications, we've found that the typical equipment used in arthroscopic surgery to be relatively heavy and sizable. Accommodating the size and weight of the equipment while maintaining as small of a footprint as possible can be a challenge. The cart must host the actual surgical equipment, such as bone shavers, fluid pumps and bags of saline, and possibly cameras, monitors, and smoke evacuation systems. The cart needs to be sturdy enough to hold heavy and bulky equipment safely while still maintaining mobility and passing all the IEC 60601-1 tests for movement over a threshold, tipping, and instability in transport.
Material choices and structural supports engineered into the cart body are both keys to providing the maximum weight limit on the smallest footprint. A sturdy base and sheet metal construction are helpful in creating the stability needed for heavier medical equipment and pumps used in arthroscopic surgery.
Key Factor #2: Ease of access to equipment
Surgical carts, above all, need to be designed to allow ease of access to the equipment for the surgeon and staff during the procedure. In addition to the actual surgical equipment, there may be a need for additional storage, such as bags of saline, replacement tubing, and attachments for the surgical equipment itself. Because it is impossible to predict the room layout and dimensions of every clinical setting, it is best to maximize the ability to access the equipment from all sides of the cart. That way, the surgeon and the rest of the surgical staff can easily manage the equipment from any angle.
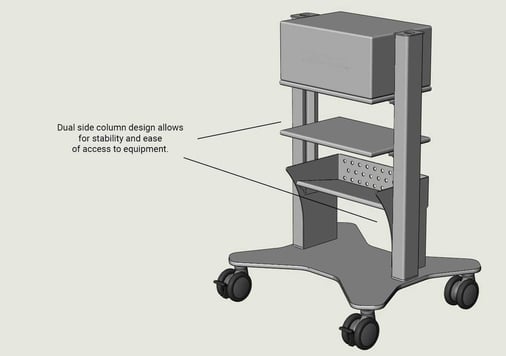
One way to ensure access at all times and in a variety of operational environments is to design the cart in such a way that the equipment can be reached from the front, rear, and sides. We have found that an open-shelf concept works well for this. One cart that we have designed with this feature is our Flexistar model standard cart: engineering the cart with two side columns rather than a central or rear column allows the middle area to remain clear to mount equipment that is accessible from the front and back.
Key Factor #3: Cord and cable management
Managing power cords, monitor connections, and surgical tubing is just as important in arthroscopy as it is in other clinical applications. If cords are not managed properly, it can put patient and provider safety at risk and increase the likelihood of damage to the medical device components.
We recommend cord wraps and voids in structural columns that can be used to house cables to help manage power cords and monitor cables. Other options to consider are simple hooks or wraps for tubing, or bins that can be used to store foot pedals and power cords when the cart is in transit.

Key Factor #4: Cleanability of the cart
Sanitization of equipment and carts is always important in the clinical space. There are design choices that can support the ease with which the cart can be cleaned by staff. We recommend minimizing the number of seams and tight clearances between surfaces to allow for easier and more thorough cleaning.
Of course, material and finish selections are also important. Work with your device cart manufacturer to select paint and finish options that will stand up to vigorous scrubbing and resist degradation from the long-term use of chemical cleaning agents. In addition, remember that any labels applied to the cart must pass the IEC 60601-1 durability of markings test. Choosing casters that resist corrosion is a good idea for arthroscopy carts as well.
Key Factor #5: Managing leakage current
All medical devices that will be subjected to IEC 60601-1 testing will need to meet leakage current standards. In some cases, the pump or surgical equipment mounted on the cart may need to use an isolation transformer to prevent dangerous current leakage in the clinical space that can harm staff or patients. Keep in mind that if your device requires an isolation transformer for this purpose, it will require not only space on the cart, but it will add considerable weight to the cart.

We developed our Flexistar standard medical cart with arthroscopic applications in mind. Flexistar was designed to be a robust platform for heavier equipment while maintaining safety and ease of use. HUI has also designed custom medical carts for arthroscopic surgical equipment with great success. If you have an arthroscopy medical cart project you’d like to consult with our team about, please reach out to MBD@huimfg.com and we’d be happy to help.

